Back to Blog

Decoding Your Credit Card Number
Structure of a Credit Card Number
Credit cards throughout the world follow the same standard for numbering.
These are drawn up by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC 7812-1:1993) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI X4.13).

Numbering System
Credit card numbers are a particular type of ISO/IEC 7812 bank card numbers, consisting of:
Major Industry Identifier (MII)
Issuer Identification Number (IIN)
Account Number
Checksum

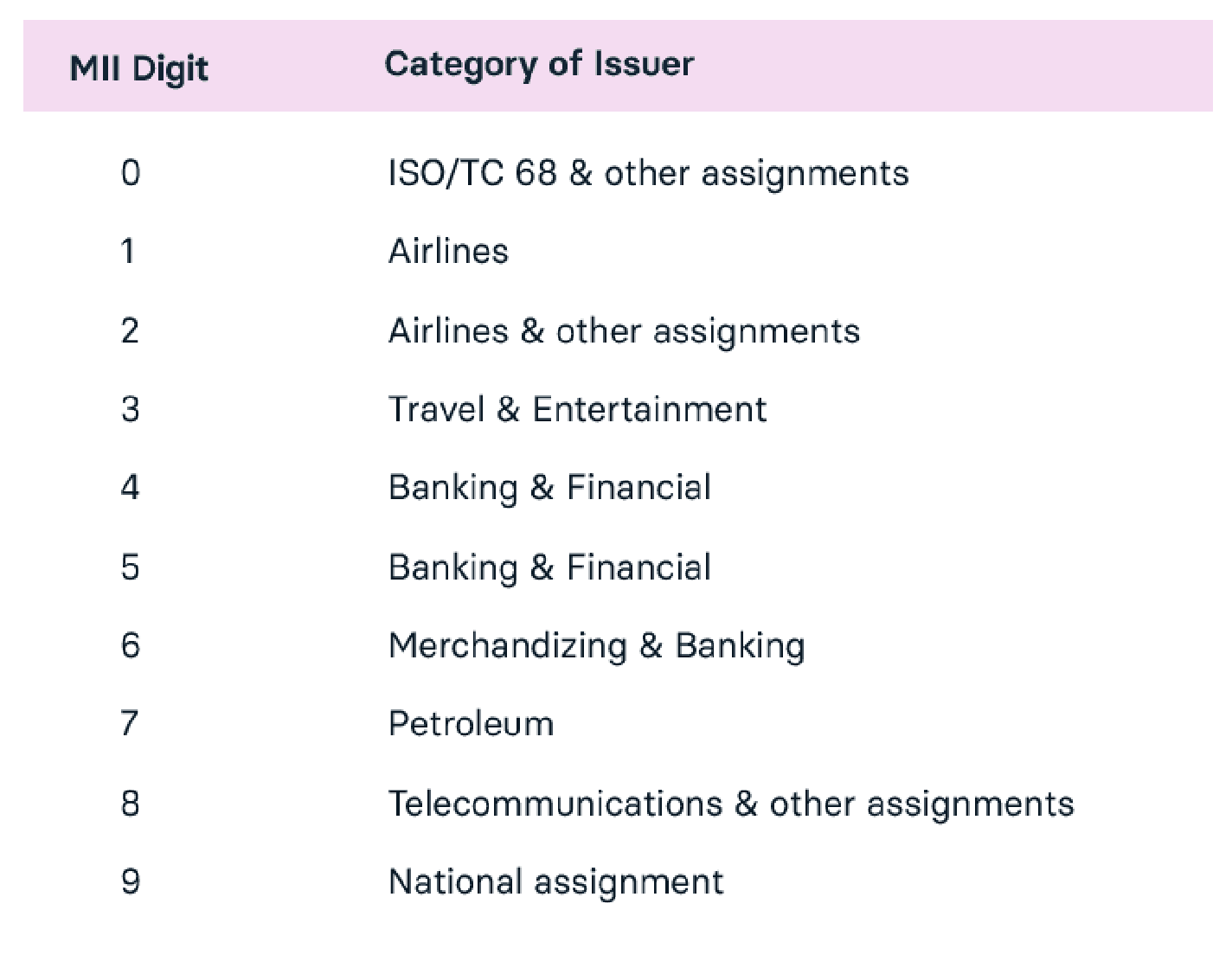
Major Industry Identifier (MII)
This is the first digit of the credit card, representing the category of the issuer.
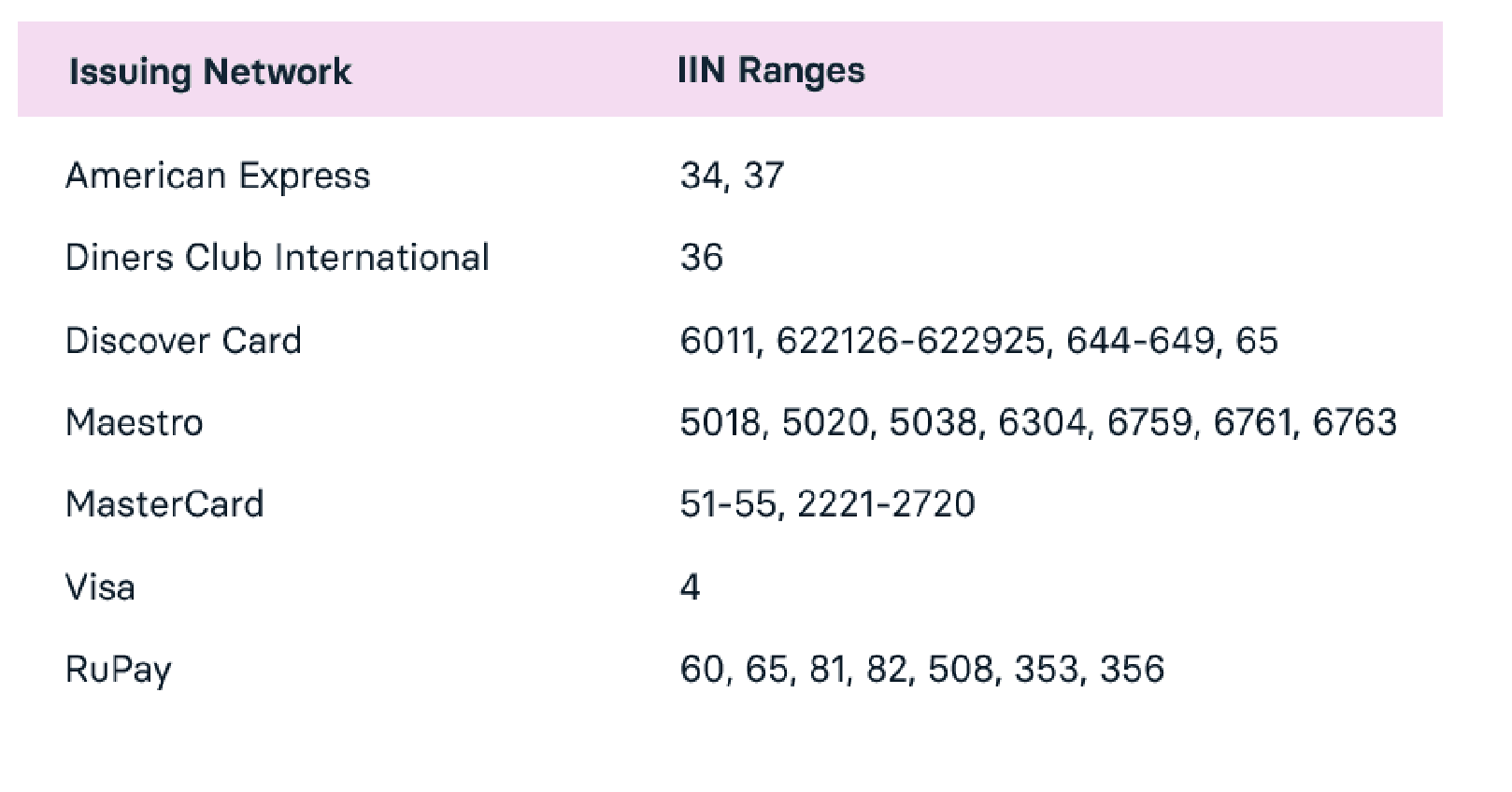
Issuer Identification Number (IIN)
The first six digits (including the MII) denote the Issuer Identification Number. It is also known as Bank Identification Number (BIN).
Account Number
The seventh digit and onwards represent the individual account number. They are unique to each cardholder and help identify the specific credit card account within the issuing bank.
The length of this number may vary depending on the issuing bank.

The Final ‘Check’ Digit
The final digit is a checksum generated using the Luhn algorithm, which helps validate the authenticity of the credit card number.
This check digit adds an extra layer of security to prevent errors and detect potential fraud.

Safety & Security
Never share your Credit Card PIN or OTP with anyone, even if it is a person claiming to be a bank representative.
Avoid using your credit card on suspicious applications or websites.
Update your bank immediately in case your card is lost or stolen.